Written by: <Authors><Author><Id>5429</Id><Name>Lipsa Mohapatra</Name><FriendlyName>lipsa-mohapatra</FriendlyName><AuthorImage>/5429/lipsa.jpg</AuthorImage></Author></Authors>

Written by: <Authors><Author><Id>5429</Id><Name>Lipsa Mohapatra</Name><FriendlyName>lipsa-mohapatra</FriendlyName><AuthorImage>/5429/lipsa.jpg</AuthorImage></Author></Authors>

Medical Textiles are a branch of technical textiles that has wide application in the medical sciences. Such textiles are more known for their technical properties rather than aesthetic values. There is a wide range of application in the medical field. Medical textiles can be used in the form of polymers, fibres, yarns and fabrics (woven, knitted, braided or nonwoven materials). The purpose of medical textiles is to provide safety, comfort, and help to heal and reduce pain of the patients.
Qualities Possessed by Medical Textiles
• High absorbency (sterilised cotton, bandage)
• Higher tenacity, extensibility, flexibility, softness and durability
• Non-toxic materials
• Non-carcinogenic
• Anti-microbial
• Hygienic products
• Nonallergic reactions
• Better comfort properties
• Protection from infection (masks, gowns, PPE Kits)
• Non-reactive or chemically inert
• Biocompatibility or bio-inert i.e., when used inside the body it should not react
• Able to be sterilised (physical or chemical process)
• Optical property (in case of contact lenses)
• Greater surface property
• Diffusion property (for controlled drug supply to the wounded or diseased area)
• High absorbency (sterilised cotton, bandage)
• Higher tenacity, extensibility and durability
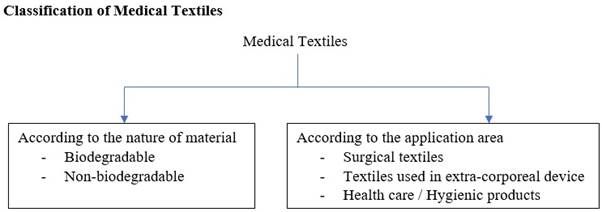
Surgical Textiles
• Implantable
• Non-implantable
1. During surgery there is a cut or an opening which is repaired, removed or replaced. Therefore, different medical textiles are used.
2. Implantable materials are those which are used inside the body. They have a wide range of restorative uses like replacing blood vessels, damaged skin, damaged heart valves and wounds. They are biocompatible, poses no risks, and are ISO certified textile materials.
3. Non-implantable materials are those that are used outside the body, compatible with the skin like bandages, surgical cotton and gauze.
4. Extracorporeal devices are those that are used for transportation of materials from outside the body to inside and vice-versa. They are used in place of non-functioning essential organs. Ex: artificial kidney, lungs, liver.
5. Healthcare/hygiene products are essential washable or single use products like masks, surgical gowns, wipes, sanitary napkins, napkins, etc. They help in preventing infection and contamination.
Biodegradable Medical Textiles
Substances which can be absorbed by the body are called biodegradable materials. These materials are absorbed within 2-3 months of its application inside the body. Ex: surgical thread.
Cotton and viscose are biodegradable, but they cannot be used in non-implantable medical textile application. Collagen is a biodegradable material which can be used in fibre/gel form. It is obtained from seaweeds. Polysaccharides, chitin or calcium alginate are biodegradable materials with good healing properties. It is used for skin dressing and as artificial skin. It adheres well to the body, forms skin simultaneously, promotes healing rate and reduces pain.
Biodegradability is carried out in two processes:
i. Decomposition
ii. Absorption
i. Decomposition – materials are degraded to monomers or oligomer (polymers having DP 7-8). It’s a two-step process – decrease in molecular chain – decrease in molecular weight. It is carried out by
• Enzymes (for implantable applications)
• Hydrolysis (for non-implantable applications)
• Oxidative action of different elements present inside the body (for non-implantable applications)
ii. Absorption – It is the process where the materials (having monomers or oligomers) are compatible with the blood type and can mix with the blood or excreted from the body in the form of urine or sweat.
Factors affecting biodegradability are:
• Chemical structure of the material
• Crystallinity
• Shape and morphology
• Hydrophilic / hydrophobic balance (when membrane allows only drugs, it behaves as a hydrophobic material).
Non-biodegradable Medical Textiles
Textiles that are not bio-degradable like polyester, polypropylene (PP), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), polyamide, polyethylene, glass, carbon and elastomeric fibres that are used for making surgical masks, caps, PPE Kits, gowns, blankets, cover drapes, surgical hosiery.
Implantable Medical Textiles
These are used in both hard and soft tissue implants.
• Hard tissues are generally orthopaedic implants like bone, teeth, bone cement, bone joints.
• Such implants have excellent mechanical properties
• Carbon composites are preferably used for such applications known as orthopaedic implants
• A nonwoven material made of graphite and Teflon is used as a coating material over the orthopaedic implants to improve tissue growth.
Soft tissue implants are generally used for skin dressing.
1. Highly flexible and pliable
2. Anti-bacterial properties
3. Prevent dehydration of wound
4. High absorbency properties to absorb wound fluids
5. Soft woven material like gauze, nonwoven materials like bandaids and microporous materials are used for such applications
6. Nature of material should be bio-degradable (enzymes), commercially available. Poly L-Leucin (polymer of natural amino acid), chitin and collagen materials are used for skin dressing.
7. Fibre property requirements for soft tissue implants are:
- Tissue compatibility
- Better water vapour transmission property as compared to normal skin
- Impermeability to microorganisms
- Prevention of wound contraction
- Flexibility and pliability to permit confirmation to irregular wound surface
- Elasticity is to permit motion of underlying body tissue.
Suture Applications
Sutures are used to close wound, join tissues (soft tissues) and tie-up bleeding vessels. Sutures can be of two types:
• Bioabsorbable suture – (collagen, chitin, polyglycolic acid are used. Chitin is the best because of its tensile properties)
• Non-bioabsorbable suture (PET, polytetrafluoroethylene, silk)
Non-Implantable Medical Textiles
These textiles find applications in the following areas:
• Wound care absorbable pads (cotton, viscose)
• Contact layer pad (silk, polyamide, viscose)
• Base material (cotton, viscose, polyamide, elastomeric materials)
• Simple bandage (cotton, viscose)
• Highly supportive/ compressive/ orthopaedic bandages (polyurethane, PP, PE, PET, viscose, cotton).
• Crepe is the best example of non-implantable textiles.
Extracorporeal Medical Textiles
• Artificial kidneys (hollow viscose fibres) – its function is to remove waste products from blood.
• Artificial levers (hollow viscose fibres) – helps to separate and disperse plasma and entry for fresh plasma.
• Mechanical lungs (hollow polypropylene and silicone membrane) – removes carbon dioxide from blood and supplies fresh blood to the vessels.
Textile Materials used for Surgical Care
• Drapes (PP, PET, viscose, cotton)
• Bedding (cotton, viscose)
• Blankets (cotton, PET (woven, knitted))
• Sheets and pillow cover (cotton, viscose)
• General clothing like uniforms (cotton, woven)
• Protective clothing like gloves (cotton, PET, rubber)
• Seats (PP, PET)
• Absorbent layer (wood pulp, nonwoven).
Thus, medical textiles find a wide range of applications in today’s world. With development of science and technology there is a huge advancement in this field. Clinical science has been greatly impacted by the use of such textile materials. These materials undergo rigorous testing by ISO so that care and quality can be assured to the users.
References:
i. Meena, C. R., Ajmera, N. & Sabat, P. K., n.d. TechnicalTexttile.net. [Online] Available at: https://www.technicaltextile.net/articles/medical-textiles-2587. [Accessed 2022].
ii. Textile Sphere, n.d. [Online] Available at: https://www.textilesphere.com/2020/03/medical-textiles.html [Accessed 2022].